A healthy smile not only provides an aesthetic appearance; it is also an indicator of an individual’s overall health. However, one of the most common oral and dental health problems faced by humans is tooth decay. So, why do our teeth decay? Is it possible to completely prevent tooth decay? In this article, we will examine what tooth decay is, how we can protect ourselves, and treatment options.
1. What is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is a disease that occurs as a result of the structural deterioration of the enamel and dentin layers of the tooth due to acids produced by bacteria.
Bacteria are present inside our mouths. When we consume sugary, starchy, and similar foods, these bacteria cause acidification. Over time, these acids damage the protective layer of the tooth, leading to the onset of decay.
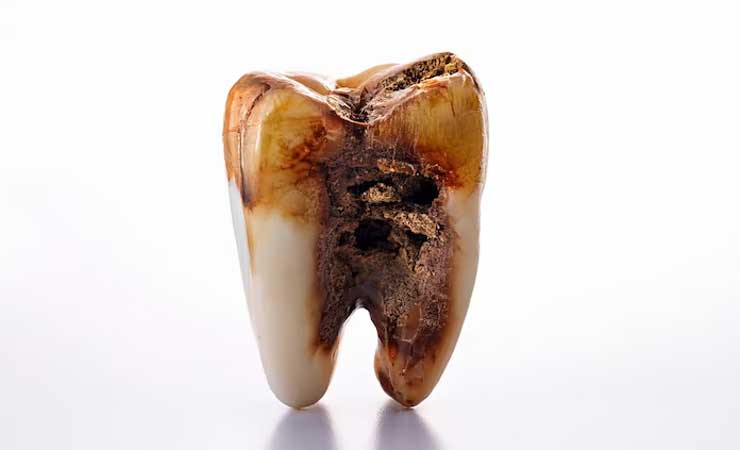
Tooth decay that occurs in the early stages often goes unnoticed. However, as it progresses, it reaches the inner layers of the tooth and causes problems. These problems can lead to pain, infection, or tooth loss. At this point, we are faced with a decayed tooth.
2. Why Do Teeth Decay? Basic Causes
There are multiple factors that play a role in tooth decay. Some of these causes are within a person’s control, while others are related to genetic predisposition:

- Poor oral hygiene: Not paying attention to oral care. These include not brushing your teeth regularly and not using dental floss. These cause bacteria to accumulate and multiply.
- Sugary and acidic foods: Sugar is a food source for bacteria. Snacks, carbonated drinks, and sticky sweets are the biggest contributors to tooth decay.
- Dry mouth: Saliva neutralizes acids in the mouth. However, if saliva production decreases due to certain medications, illnesses, or stress, the risk of tooth decay increases.
- Fluoride deficiency: Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and increases its resistance to acid attacks. People who do not use fluoride products are more prone to tooth decay.
- Genetic factors: It should be noted that individuals with a family history of tooth decay may be more susceptible to tooth decay.
3. What are the symptoms of tooth decay?
Tooth decay usually starts insidiously. It may not show any symptoms in the early stages. However, as the process progresses, some warning signs appear:

- Tooth sensitivity
- Tooth pain or throbbing
- Dark spots on the tooth surface
- Discomfort while chewing
- Bad breath
- A change in taste in the mouth
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a dentist without delay. This is because cavities detected in the early stages can be treated with a simple filling, but if left untreated, more invasive procedures such as root canal treatment or tooth extraction may be necessary.
4. How Can Tooth Decay Be Prevented?
The good news is that tooth decay is largely preventable. The following habits will help you build a strong defense against tooth decay:

- Brush your teeth twice a day: Brush your teeth for at least two minutes in the morning and evening with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Use dental floss: Toothbrushes cannot reach the surfaces between your teeth. Dental floss or interdental brushes prevent plaque buildup.
- Limit sugar intake: Avoid sugary foods, especially between meals. If you must eat sweets, we recommend doing so during a main meal.
- Drink plenty of water: Water reduces acidity and promotes saliva production.
- See your dentist regularly: Visit your dentist every six months. This allows cavities to be detected before they develop.
- Get fluoride support: If recommended by your dentist, you can strengthen your tooth enamel with professional fluoride treatments.
In addition, “fissure sealants” for children protect newly erupted molars from decay. If you pay attention to the points mentioned above, you will significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay.
5. How are decayed teeth treated?
The treatment method varies depending on the extent of the decay:
- Superficial decay: Fluoride supplements and small fillings may be sufficient.
- Moderate decay: The decayed tissue is cleaned and filled.
- Advanced decay: If the decay has reached the nerves, root canal treatment is required.
- In cases where the tooth cannot be saved: The tooth is extracted and replaced with a prosthesis such as an implant or bridge.
Untreated tooth decay can affect not only oral health but also many other systems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and digestive problems. Therefore, it should not be neglected.
Be Strong Against Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a health issue that cannot be ignored but is largely preventable. Maintaining good oral hygiene, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and adopting healthy eating habits are the most effective ways to prevent tooth decay. Remember, healthy teeth are not just about a beautiful smile—they are the key to a healthy life.


