Table of Contents
ToggleTeeth whitening care begins after treatment and determines how long the color will last. The whitening effect is not stable in the first few days. The pores are temporarily more open. Susceptibility to staining increases. Managing this period correctly ensures lasting brightness. Color stability is achieved through a combination of proper nutrition, regular hygiene, and remineralization.
Abrasive products should be limited. Reducing acid load is important. Brushing technique and the type of toothpaste used affect the result. Home-based support should be applied in a controlled manner. Clinical control stabilizes the color. Below, you will find steps that can be applied in your daily routine. Proceed with short, clear, and sustainable recommendations. Even small changes make a big difference. Plan your actions. Establish a disciplined routine. Maintain the color for longer.
What is color stability and why is it critical?
Teeth whitening care color stability is the durability of the achieved shade over time. The gel leaves temporary porosity in the enamel. In the first few hours, the coloring molecules adhere easily. That is why early management is so important. Stability develops with mineral balance, saliva buffering power, and mechanical cleaning. As acid and pigment load increase, color reversal accelerates. Abrasive habits weaken the enamel. Remineralizing ingredients close the pores. This balances light reflection. Brightness is preserved. You can support this balance with simple rules. Discipline is required in the short term. In the long term, a sustainable routine brings success. A clinical follow-up plan ensures this process. Color stability is achieved through conscious steps.

- Goal: reduce color fluctuation in the first 2 weeks
- Focus: acid/pigment contact, remineralization
- Result: a more lasting and natural-looking tone
First 48 hours: Critical period management
The first 48 hours of teeth whitening care is the “white diet” period. During this time, the porous structure is at its highest. Coffee, tea, cola, red wine, and colored sauces accelerate staining. Smoking and temperature differences increase sensitivity. Choose lukewarm water. Acidic drinks remove calcium from the enamel. Therefore, limit soda and lemon-based drinks.
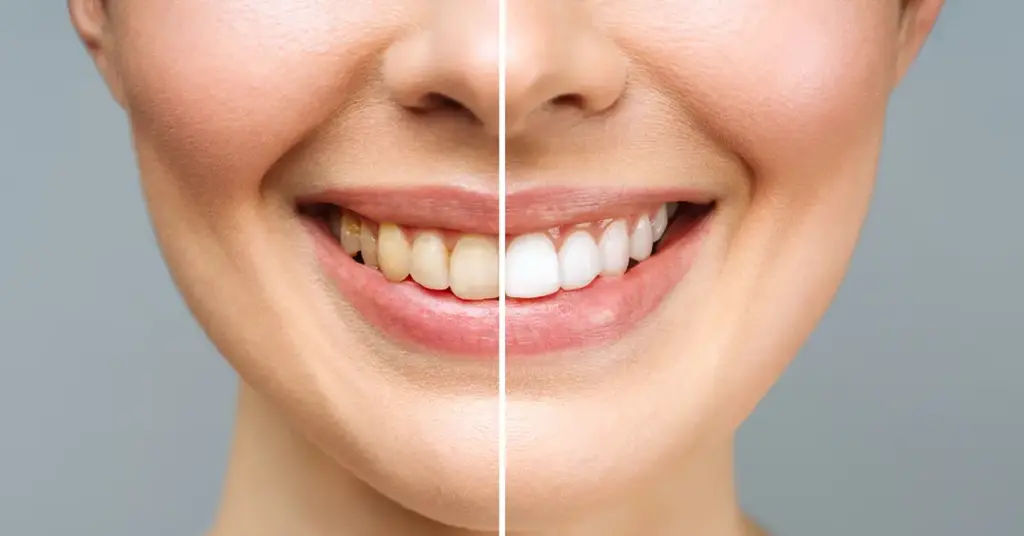

Brushing should be gentle. Abrasive particles damage the new color. Use supports containing fluoride or hydroxyapatite. Dental floss and interdental brushes reduce plaque retention. Mouthwash should be alcohol-free. If you used a splint the first night, continue as recommended by your dentist. If you have bruxism, a protective plate indirectly contributes to color stability.
- “White diet”: colorless, soft, warm options
- Contact with coloring agents: minimal and short-term
- Plaque control: soft brush, gentle technique
Diet and beverage control
Teeth whitening care during the diet plan determines the fate of the color. Time high-pigment foods. Drink coffee with a straw and quickly. Then rinse with water. Consume acidic beverages with meals. Drinking them alone increases demineralization. Yogurt and cheese provide calcium. They support the buffering power of saliva. Fibrous vegetables provide a mechanical cleaning effect. Avoid hot-cold shocks. Enamel expansion can trigger microscopic cracks. Reduce sugar consumption. Plaque acidity increases. Color reversal accelerates. Wait 30 minutes after meals before brushing. Brushing immediately can deepen the acid effect. Drinking water throughout the day is simple but very effective.

- “Straw rule”: minimize contact with coffee/tea
- “Water barrier”: drink water after every colored beverage
- “Meal rule”: do not drink acidic beverages alone
Oral hygiene routine and product selection
Teeth whitening care depends on routine for long-lasting results. Choose a soft-bristled brush and small head. Focus on the plaque line using the Bass technique. Avoid abrasive toothpastes. Products with low RDA values are safe. Fluoride, nHAP, or calcium-phosphate complexes strengthen enamel. Do not overuse daily peroxide products. Sensitivity increases if balance is disrupted.

Dental floss and interdental brushes support color stability. As plaque decreases, staining adhesion decreases. Alcohol-free mouthwashes are gentler on tissues. Electric brushes control time and pressure. They prevent excessive pressure. Tongue cleaning reduces volatile sulfur compounds. Brightness perception increases. Results are lasting when the routine is sustainable.
- Paste selection: low RDA, remineralizing
- Brushing: twice a day, 2 minutes
- Completion: dental floss + interdental brush + tongue scraper
Sensitivity management and remineralization
Teeth whitening care may cause sensitivity. This is related to temporary porosity and open dentin tubules. Products containing potassium nitrate soothe nerve transmission. nHAP and calcium-phosphate-based agents seal the tubules. Fluoride varnish provides rapid relief in the clinic. Reducing acid load decreases sensitivity. Avoid very cold beverages. Thermal shocks exacerbate microscopic cracks. Nighttime splint use limits bruxism-related wear. Increase water consumption for rehydration. Saliva is a natural buffer and mineral source. If you have dry mouth, talk to your dentist. Use saliva-enhancing products if necessary. As sensitivity decreases, brushing quality improves. The color also becomes more permanent.
- Sensitivity reducers: potassium nitrate, nHAP, fluoride
- Triggers: acid, cold, aggressive brushing
- Support: varnish applications and night guard
Clinical control, touch-ups, and sustainability
Teeth whitening care plan is completed with periodic check-ups. A short check-up appointment in the first month is ideal. Plaque, diet, and product compatibility are evaluated. Polishing is performed if necessary. Low-concentration touch-up gels can be applied to micro-stains. Home trays are used according to the dentist’s protocol. Frequency is individualized. If there is smoking, pigmented diet, and bruxism, the interval is shortened. Professional cleaning removes the staining film. Brightness increases immediately. Photo-based shade tracking provides motivation. The goal is balanced maintenance, not aggressive whitening cycles. Small but consistent steps yield the best results. Proper follow-up keeps the color natural and healthy.
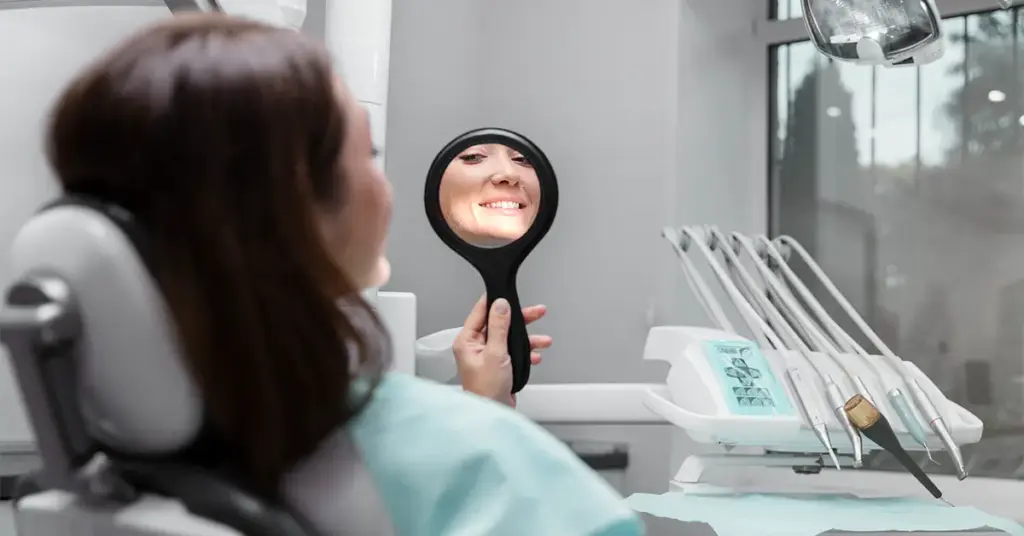

- Follow-up interval: 1st month, then 6–12 months
- Touch-up: low dose, short duration, under dentist supervision
- Monitoring: photo shade scale, habit update
Mini Checklist
- Follow a “white diet” for the first 48 hours.
- Consume acidic beverages with meals. Then drink water.
- Use low RDA toothpaste + dental floss + interdental brush.
- For sensitivity, choose potassium nitrate or nHAP.
- Do not skip regular clinical check-ups.